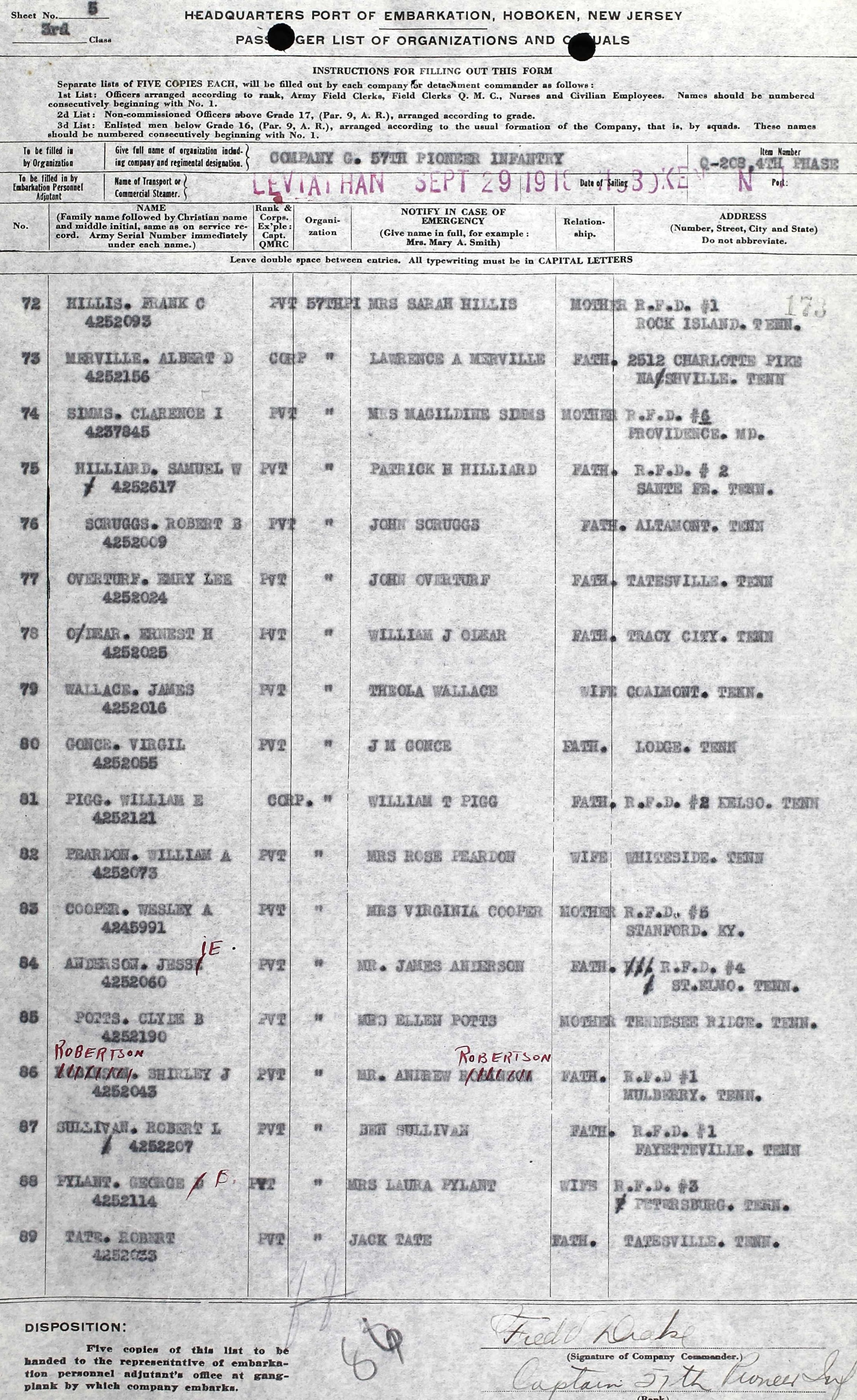
The Engineers’ Line
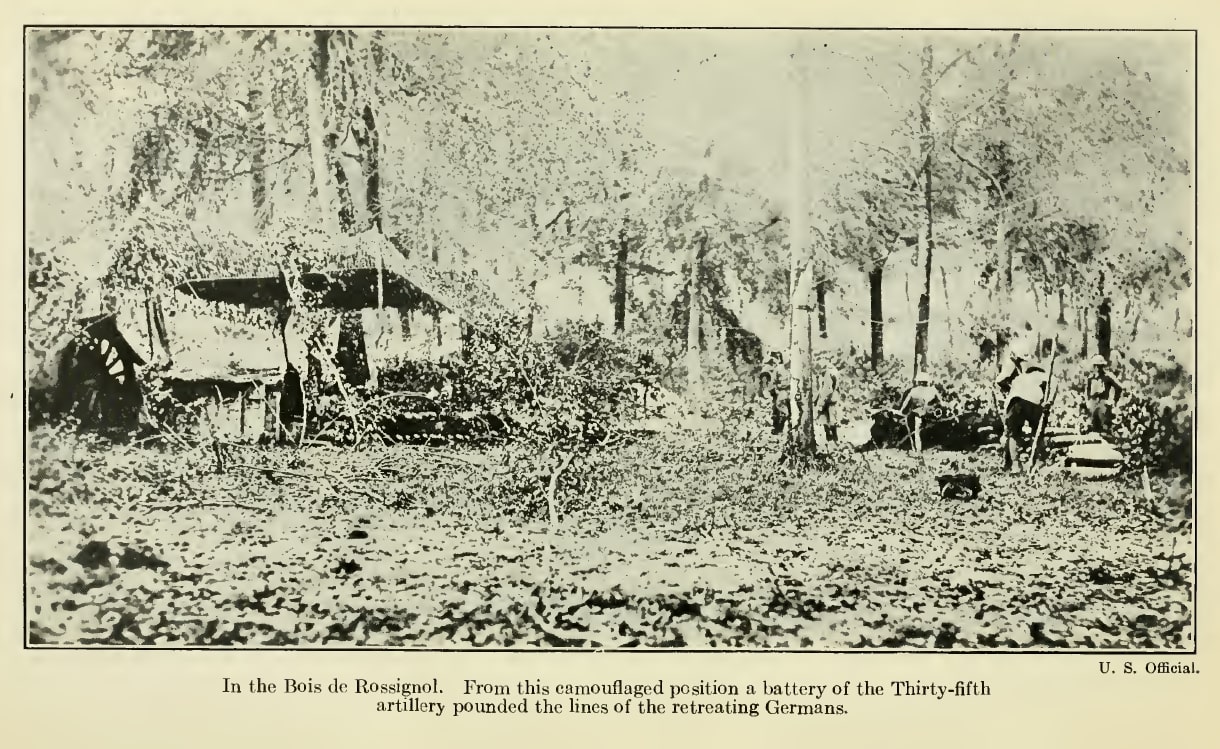
September 30, 1918, what was left of the 35th Division lay in defensive positions built by the 110th Engineers the previous day. These were a long series of short, shallow trenches, not man-height but deeper than a foxhole, from which the troops might repulse a counterattack. The division would lay here throughout the day, under continuing shell fire.
During the first three days of the advance, the 110th Engineer Regiment’s job was to build and repair roads for horse-drawn vehicles, which brought ammunition, rations, and equipment from the rear. Behind the front lines, the engineers filled a noncombatant role.
At 10:00 p.m. September 28, by order of General Traub, the 110th Engineers were made division reserve, therefore, combatants, and equipped with rifles, ammunition, and grenades.
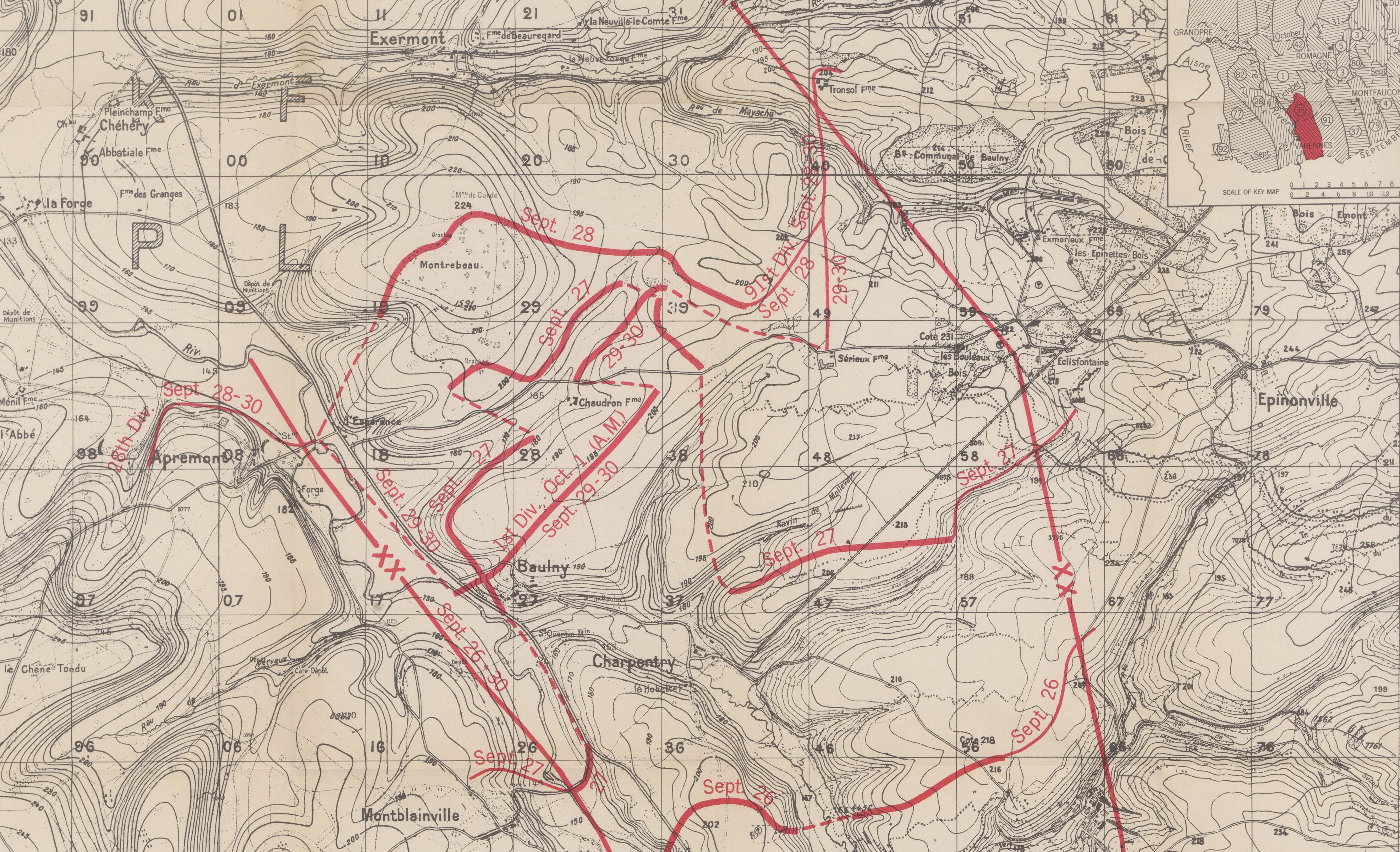
The next day, under constant artillery fire, the engineers dug three kilometers (almost two miles) of trenches from Baulny to Sérieux Farm. When the digging was done, they dropped into the trenches, exchanged shovels for rifles, and pointed them north. Throughout the afternoon and evening of the 29th, as the exhausted infantrymen arrived from Exermont and Montrebeau Wood, the engineer officers placed them in the line.
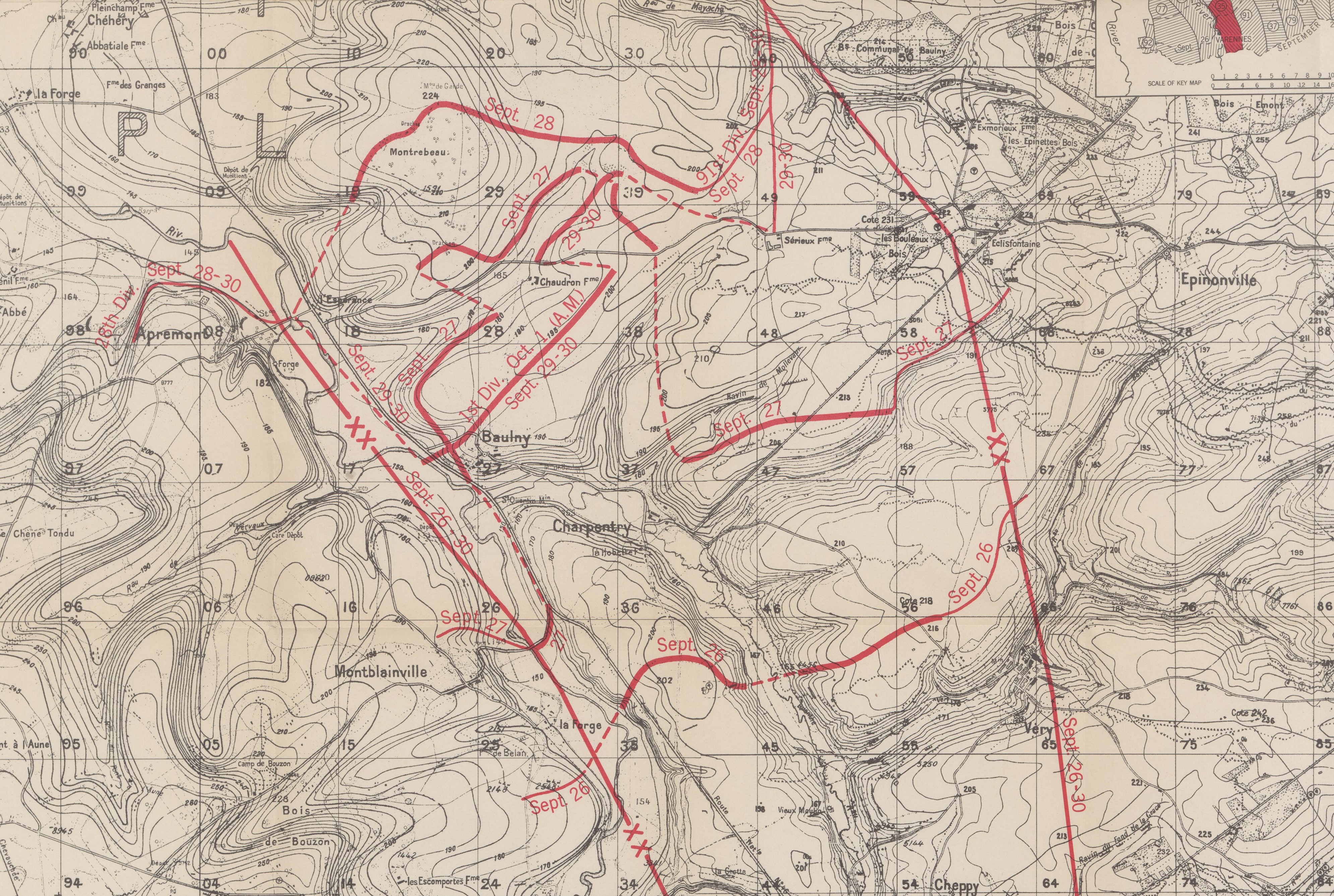
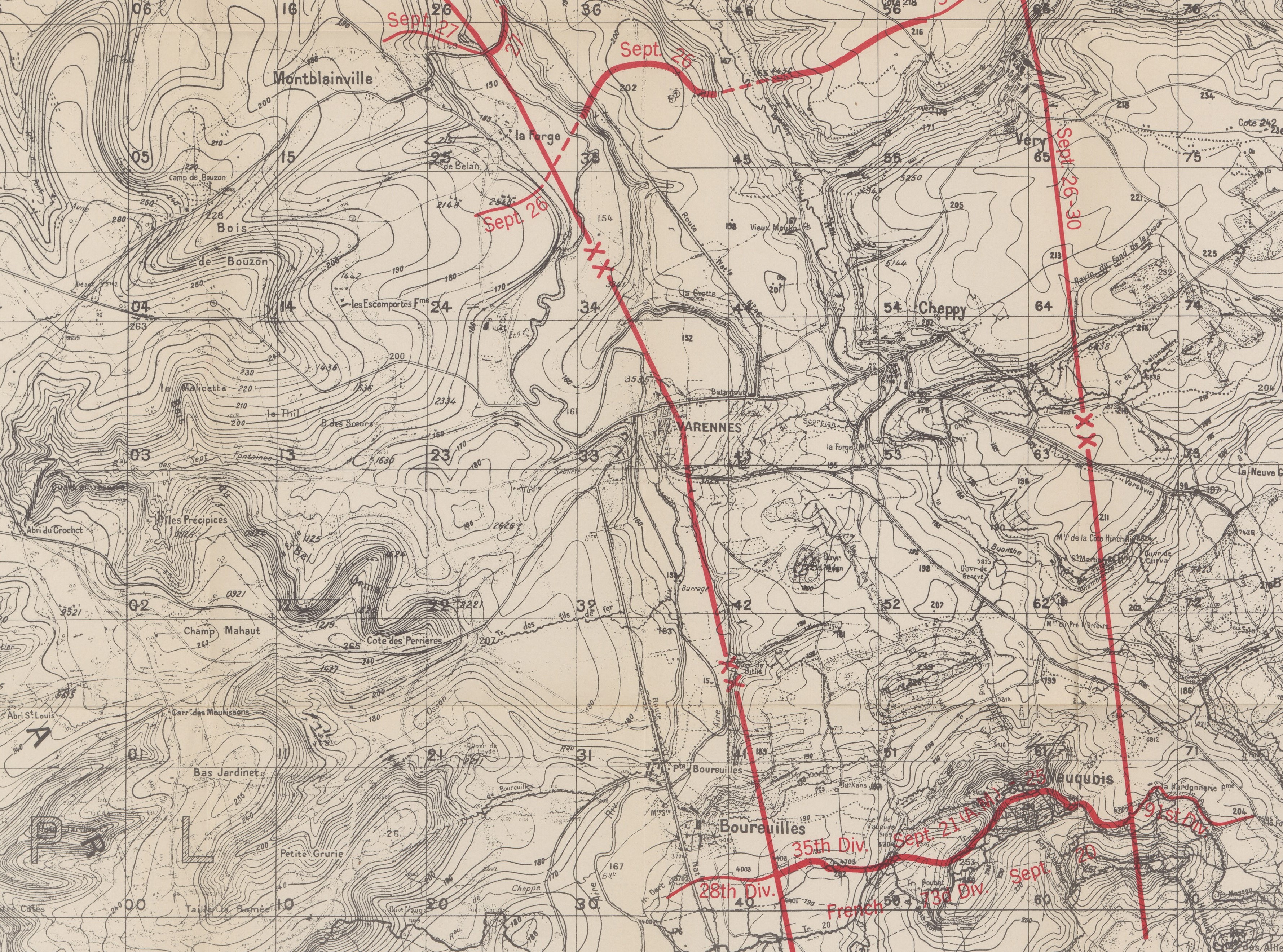
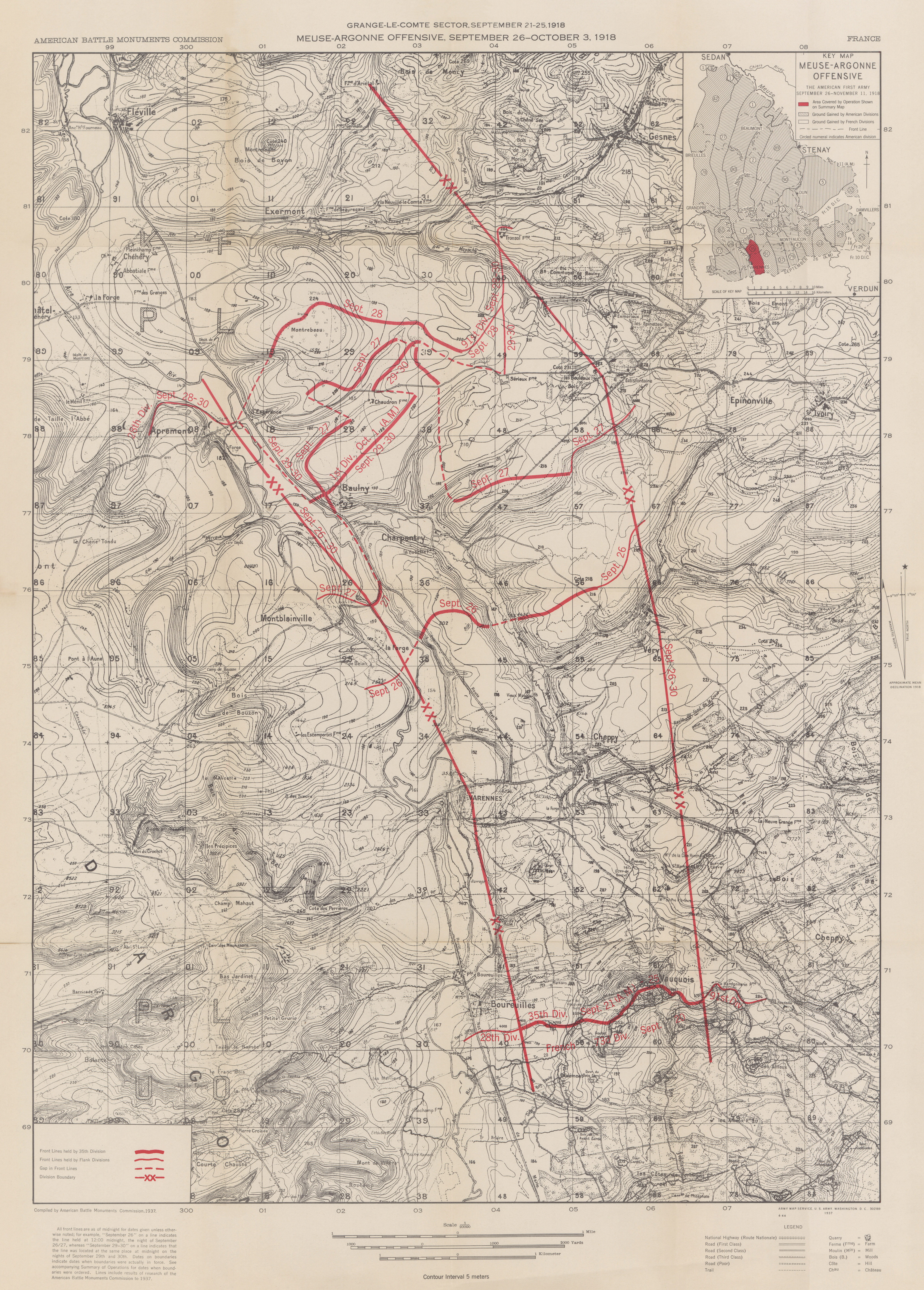
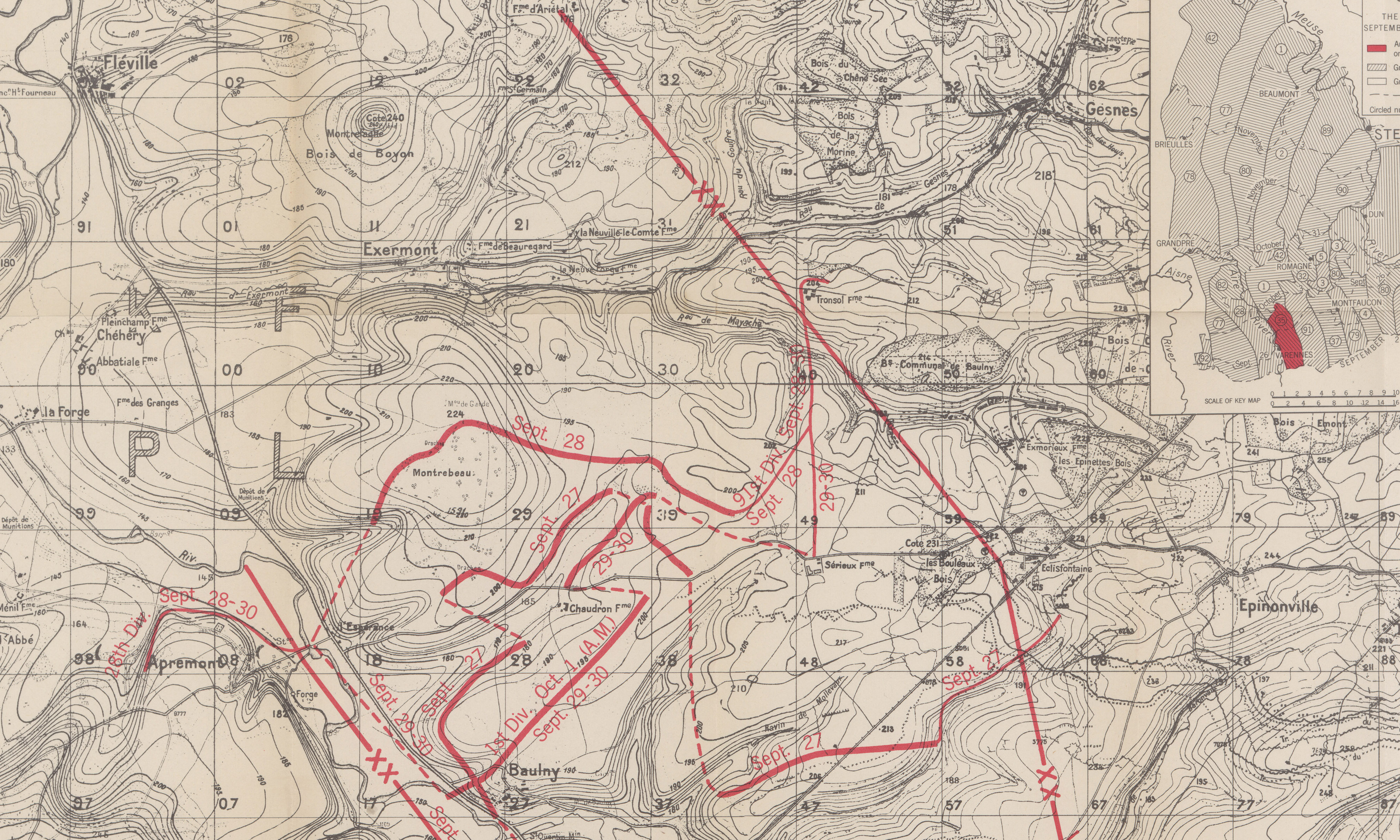 Map section, September 30, 35th Division, Grange le Comte Sector, Meuse-Argonne, American Battle Monuments Commision 1937
Map section, September 30, 35th Division, Grange le Comte Sector, Meuse-Argonne, American Battle Monuments Commision 1937
Kenamore calls September 30 “a desperate day.” The few remaining officers tried to organize the line for defense, but in some parts of the trenches, the troops were too bunched up; one artillery shell could take out several men. In other parts, they were too thin; machine gunners held sections without riflemen in support. Fatigued, hungry, thirsty, sleep-deprived, many suffering from dysentery, the men had reached the physical limit of functioning.
“Despite all the men could do to fulfill the dictates of duty, the supreme weariness of the last four days of fighting, now entering on the fifth, was not to be easily triumphed over. What they did was by sheer will, for bodies were numb and reacted slowly to thoughts that would drive them.” (Hoyt 119)
That day, three counterattacks were launched on the trenches by a determined enemy. Three counterattacks were repulsed. With the strength of will left in them, the men of the 35th held the Engineers’ line.
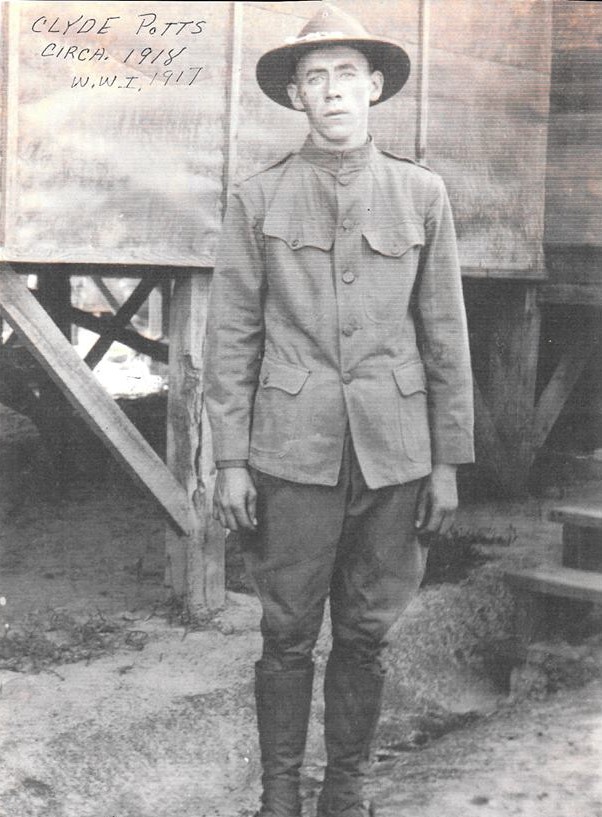
My great grandfather, like many veterans, didn’t talk much about his wartime experience. His family has only his discharge paper and a few anecdotes.
One hundred years later, I’ve discovered a few documents that bear his name. From draft registration to discharge, I’m following the paper trail of B. F. Potts’s journey to the battlefields of the Great War in France and back home again.
Previous articles:
“Well, Daddy, what did you think about France?”
“It's a very muddy place.”
Benjamin Franklin Potts Registers for the Draft
As the Great War thundered across the fields of northern France, ten million American men, ages 21 to 30, signed their names to register to be drafted into military service.
Military Induction and Entrainment
“I, Benjamin Franklin Potts, do solemnly swear to bear true allegiance to the United States of America, and to serve them honestly and faithfully, against all their enemies or opposers whatsoever…”
“If it moves, salute it. If it doesn’t move, paint it!”
Embarkation, the Tunisian, and the Bridge of Ships
In his first ocean voyage, B. F. Potts crossed the submarine invested waters of the North Atlantic in a convoy of steamers escorted by a warship.
Enterprise, Tennessee: The Town That Died
Grandpa owned matched pairs of horses. Him and the boys [Ben and his brothers] cut and snaked logs out of the wood to the roads. He got a dollar a day plus fifty cents for the horses.
Rendezvous with the 35th Infantry Division
“Some of the guys disobeyed orders, went into the town, broke into a bakery, and stole all the bread and baked goods…”
The battle of Saint-Mihiel (September 12-15) would be Pershing’s first operation as army commander. He assigned the 35th to the strategic reserve, whose purpose is to replace a weakened unit or to fill any gap in the line created by the enemy.
“Private Potts, how tall are you?”
The soldier, looking into a button of the captain’s coat, says, “Five foot three, sir.” The wide brim raises.
On the front now, the 35th was in range of artillery fire, and enemy planes made nighttime bombing raids over the countryside.
Planning the Meuse-Argonne Offensive
On the left, the 137th would take the “V of Vauquois,” a formidable network of trenches, zig-zagging from the hill’s west flank to the village of Boureuilles, a mile away.
The gun jumps, the earth shudders, a shock wave shatters the air and accompanies a roar that bursts between the ears. Powder fumes permeate the air. Explosions count seconds across unending darkness.
…up until 7:40 a.m. when the rolling barrage ceased, we can follow Private Potts’s movement across the battlefield.
Scrawling in a notepad, the commander tears the sheet, folds it, and thrusts it into the runner’s hands.
“Potts, take this message to brigade. Tell them we need artillery now. Go!”
“Let him lie in an artillery shower all night, if you must. But do not disturb a soldier’s sleep, sir, with your orders that change from one minute to the next!”
By morning’s end, the intermingled 137th and 139th regiments gained 500 meters and dug in before Montrebeau Wood. Through the woods and German machine-gun nests and sniper fire, the men fought in the afternoon.
“When I asked him [Grandpa Ben] if he killed anyone, this is what he told me…”
As the men would destroy one machine-gun nest, other enemy gun crews were setting up on both sides of their skirmish line.
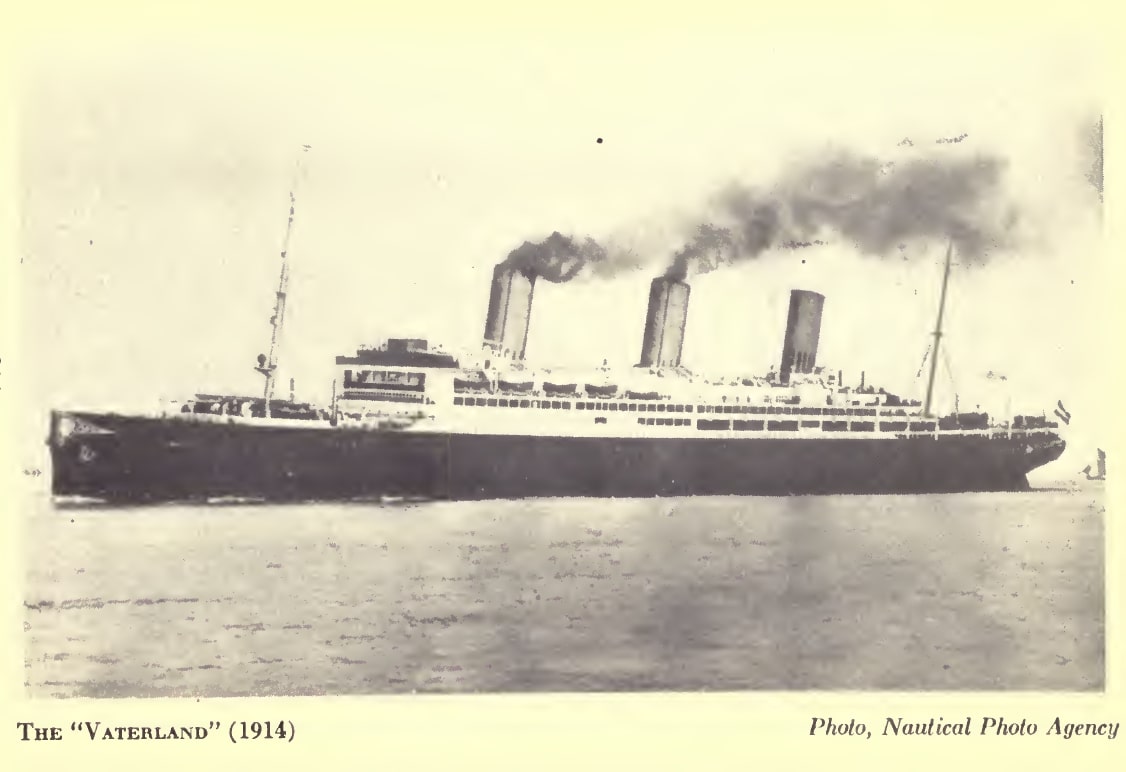
Clyde Brake Boards the Leviathan
In the morning of April 6, 1917, the day the US declared war on the German Empire, American army troops seized the Vaterlund at its mooring in the Hoboken harbor.
Next date:
October 1—Relieved